Introduction: The Invisible Power Around You
You know what’s interesting? Right now, as you’re reading these words, invisible waves are passing straight through your body. No, this isn’t science fiction, and no, you’re not turning into a superhero—although that would be nice. It’s the electromagnetic spectrum at work.
We don’t see it. We don’t hear it. Most of the time, we don’t even think about it. But without the electromagnetic spectrum, your phone wouldn’t work, Wi-Fi would disappear, medical imaging would fail, and sunlight wouldn’t warm your skin. Actually, life as we know it would feel… well, impossible.
And trust me, once you truly understand how the electromagnetic spectrum works, you’ll start noticing it everywhere—from your microwave to the colors of a rainbow. So let’s break it down in a simple, human way. No complicated physics degree required.
What Is the Electromagnetic Spectrum?
A Simple Explanation (No Jargon, Promise)
At its core, the electromagnetic spectrum is the complete range of electromagnetic waves. These waves are forms of energy that travel through space at the speed of light. They don’t need air or any physical medium. They just move.
And here’s the key idea:
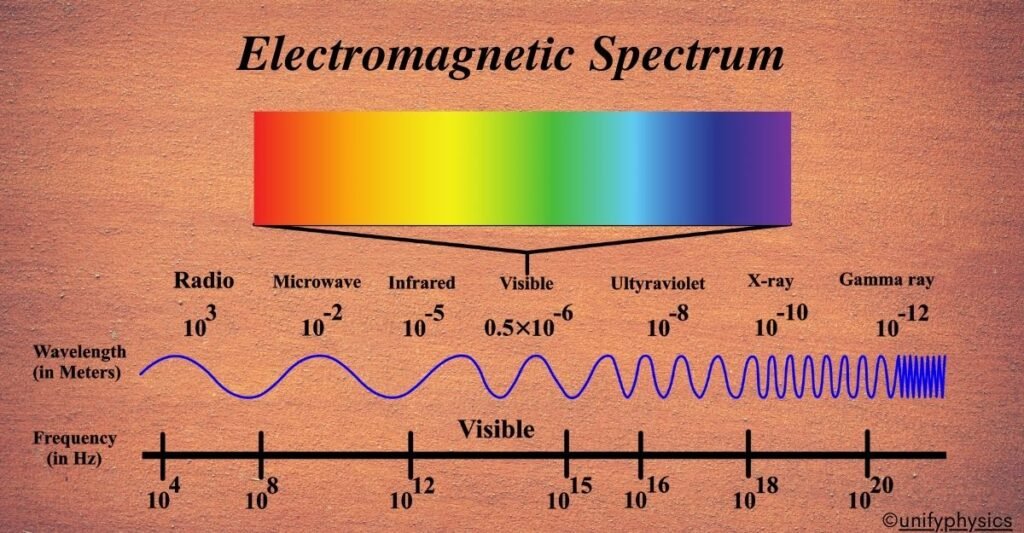
All electromagnetic waves are the same type of energy, but they differ in wavelength, frequency, and energy.
Think of it like music. Every song is sound, right? But bass notes are low and slow, while high-pitched notes vibrate quickly. The electromagnetic spectrum works in a very similar way.
Some waves are long and gentle. Others are short and incredibly powerful. Together, they form the electromagnetic spectrum.
Why the Electromagnetic Spectrum Matters More Than You Think
We’ve all been there—scrolling on our phones, watching TV, heating leftovers, or getting an X-ray at the hospital. Guess what connects all these things?
Yep. The electromagnetic spectrum.
It’s the backbone of modern technology, medicine, communication, astronomy, and even climate science. Without it, smartphones would be silent bricks, and doctors would be working in the dark—literally.
Understanding Electromagnetic Waves
Wavelength, Frequency, and Energy (Made Easy)
Let’s clear up three terms you’ll see everywhere when talking about the electromagnetic spectrum:
- Wavelength: The distance between wave peaks
- Frequency: How many waves pass a point per second
- Energy: The power carried by the wave
Here’s the simple rule:
- Longer wavelength = lower frequency = lower energy
- Shorter wavelength = higher frequency = higher energy
And yes, this difference is what separates radio waves from dangerous gamma rays.
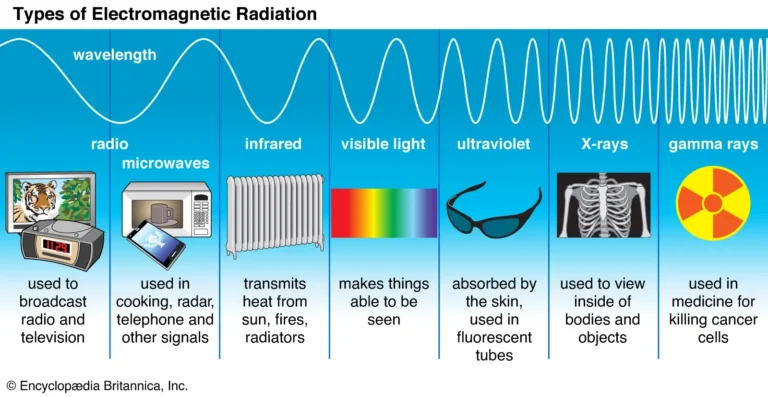
The Full Range of the Electromagnetic Spectrum (From Low to High Energy)
Now let’s walk through the electromagnetic spectrum step by step, from the lowest energy waves to the most powerful ones.
Radio Waves: The Gentle Giants
What Are Radio Waves?
Radio waves sit at the low-energy end of the electromagnetic spectrum. They have long wavelengths and low frequencies, which makes them incredibly safe.
Actually, radio waves are so gentle that they pass through buildings, walls, and even your body without causing harm.
Everyday Uses of Radio Waves
Radio waves power:
- AM and FM radio
- Television broadcasts
- Mobile phone communication
- GPS signals
- Wi-Fi and Bluetooth
So the next time your phone rings or your Wi-Fi connects instantly, remember—radio waves are quietly doing the heavy lifting.
Microwaves: Not Just for Your Kitchen
What Makes Microwaves Special?
Microwaves are a subset of radio waves but with higher frequency and energy. They’re still safe at everyday exposure levels, but powerful enough to heat food.
That’s why your microwave oven works so fast—it excites water molecules, generating heat.
Where Microwaves Are Used
Microwaves are used in:
- Microwave ovens
- Satellite communication
- Radar systems
- Weather forecasting
- Wireless internet
And honestly, weather radar alone makes microwaves incredibly valuable. They help save lives by predicting storms before they hit.
Infrared Radiation: The Heat You Can’t See
Feeling Infrared Without Seeing It
Ever stood near a fire and felt warmth on your skin? That’s infrared radiation, another key part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
Infrared waves are just below visible light in energy. We can’t see them, but we definitely feel them.
Infrared in Daily Life
Infrared radiation is used in:
- TV remote controls
- Thermal cameras
- Night vision equipment
- Heat sensors
- Medical therapies
And here’s something cool—animals like snakes can see infrared radiation, allowing them to detect warm prey in total darkness.
Visible Light: The Tiny Slice We See
The Only Part Our Eyes Can Detect
You know what’s wild? Visible light is just a tiny fraction of the electromagnetic spectrum. Yet, it’s the part that shapes our entire visual experience.
From red (lower energy) to violet (higher energy), visible light allows us to see colors, shapes, faces, and sunsets.
Why Visible Light Is So Important
Visible light:
- Enables human vision
- Drives photosynthesis
- Influences mood and sleep cycles
- Helps astronomers study stars and galaxies
Without visible light, the world would exist—but we wouldn’t experience it.
Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation: Helpful and Harmful
The Double-Edged Sword
Ultraviolet radiation sits just beyond visible light. It has higher energy, which means it can interact more strongly with living cells.
And yes, this is where caution comes in.
Benefits and Risks of UV Radiation
Benefits:
- Helps the body produce vitamin D
- Used in sterilization and disinfection
- Treats certain skin conditions
Risks:
- Sunburn
- Skin aging
- Increased risk of skin cancer
So while UV radiation isn’t evil, balance is everything. Sunscreen exists for a reason.
X-Rays: Seeing Inside the Human Body
How X-Rays Work
X-rays are high-energy electromagnetic waves that can pass through soft tissue but are absorbed by denser materials like bone.
That’s exactly why doctors use them to see fractures, infections, and internal injuries.
Uses of X-Rays Beyond Medicine
X-rays are also used in:
- Airport security scanners
- Industrial inspection
- Astronomy
- Art restoration
They help us see the unseen—safely, when used correctly.
Gamma Rays: The Most Powerful Waves
The Extreme End of the Electromagnetic Spectrum
Gamma rays sit at the highest energy end of the electromagnetic spectrum. They have extremely short wavelengths and immense energy.
They’re produced by:
- Nuclear reactions
- Supernova explosions
- Radioactive decay
Gamma Rays in Medicine and Science
Despite their power, gamma rays are used carefully for:
- Cancer treatment (radiation therapy)
- Sterilizing medical equipment
- Scientific research
Handled properly, even the most intense energy can be life-saving.
Electromagnetic Spectrum and Modern Technology
Why Our Digital World Depends on It
Smartphones, satellites, streaming services, GPS navigation—none of these exist without the electromagnetic spectrum.
Every text message, video call, and online search travels as electromagnetic waves before reaching its destination.
And honestly, that’s kind of magical.
Is the Electromagnetic Spectrum Dangerous?
Clearing Up Common Myths
Let’s be real—people worry about radiation. But not all radiation is harmful.
- Non-ionizing radiation (radio waves, microwaves, visible light) is generally safe.
- Ionizing radiation (X-rays, gamma rays) can be harmful at high exposure levels—but is safe when controlled.
So no, your Wi-Fi router isn’t secretly harming you. Science has your back on this one.
The Electromagnetic Spectrum in Space and Astronomy
How Scientists Study the Universe
Astronomers use the full electromagnetic spectrum to study space. Different wavelengths reveal different secrets.
- Radio waves show cold gas clouds
- Infrared reveals star formation
- Visible light shows galaxies
- X-rays and gamma rays expose black holes
Without the electromagnetic spectrum, we’d know almost nothing about the universe.
Conclusion: Why the Electromagnetic Spectrum Truly Matters
So here we are.
The electromagnetic spectrum isn’t just a physics topic from a textbook—it’s the invisible foundation of modern life. From the warmth of sunlight to the signal on your phone, it quietly powers everything we rely on.
Once you see it this way, the world feels a little more connected. A little more amazing.
And honestly? The next time you heat food, scroll online, or step into sunlight, you’ll know exactly what’s happening—and why it matters.
FAQs About the Electromagnetic Spectrum
1. What is the electromagnetic spectrum in simple words?
The electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of invisible energy waves, including radio waves, light, X-rays, and gamma rays.
2. Which part of the electromagnetic spectrum is visible to humans?
Only visible light, ranging from red to violet, can be seen by the human eye.
3. Is electromagnetic radiation harmful?
Some high-energy radiation like X-rays can be harmful at high levels, but everyday exposure to radio waves and visible light is generally safe.
4. Why is the electromagnetic spectrum important?
It powers communication, medical imaging, technology, astronomy, and supports life on Earth through sunlight.